In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, enterprises rely on machines, tools, and infrastructure to operate efficiently. However, when assets fail to function properly, production comes to a halt, resulting in significant losses. The Intelligent Asset Performance Management (IAPM) process is critical to achieving a significant impact.
The IAPM process alters the way an organization approaches maintenance, anticipates equipment failures, and ultimately enhances reliability. With the use of a combination of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and massive data analytics, IAPM allows organizations to make more intelligent, timely, and informed decisions based on data.
This article explains what IAPM is, how it works, its components, advantages, and its future direction.
Understanding Intelligent Asset Performance Management
Intelligent Asset Performance Management (IAPM) is a new paradigm that leverages connected devices, real-time information, and sophisticated analytics to monitor, optimize, and enhance the performance of physical assets, including machinery, equipment, and infrastructure.
All changes involve shifting from traditional asset management, which reacts only to failure, to IAPM, emphasizing the anticipation of failures before they occur, ultimately assisting organizations in reducing downtime, saving money, and maximizing the lifespan of their assets.
In basic terms, IAPM enables organizations to make decisions based on data and act quickly on live insights
👉 Also Read: The Difference Between APM and ALM – Understand how Asset Performance Management (APM) compares to Asset Lifecycle Management (ALM) and how they work together for business success.
Why Intelligent Asset Management Matters
The management of assets has always been a crucial aspect of any operation, particularly in the energy, manufacturing, and logistics industries. However, as the sophistication of equipment increases and measurement becomes more data-driven, managing assets manually is no longer sufficient.
Intelligent Asset Performance Management (IAPM) enhances asset management by making it more intelligent and proactive. IAPM allows companies to:
- Analyze equipment health in real time.
- Predict when an asset is likely to fail.
- Schedule maintenance only when necessary to minimize excess costs.
- Maximize operational efficiency and equipment uptime.
The shift from reactive maintenance to predictive maintenance is what makes IAPM a crucial component of digital transformation for industries worldwide.
Key Components of Intelligent Asset Performance Management
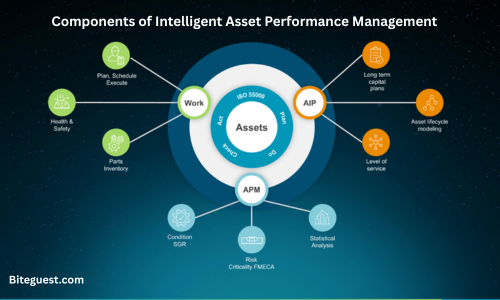
Now let’s consider the primary technologies that underpin IAPM and how these technologies coordinate to provide intelligent asset management:
1. Internet of Things (IoT) and Sensors
The Internet of Things (IoT) is integral to IAPM. Internet of Things devices and sensors are attached to assets to provide real-time data such as temperature, vibration, speed, or pressure.
For example, in a manufacturing plant, sensors can tell if a machine is overheating or vibrating unusually, both indications that a failure may be imminent. This data facilitates teams to respond before a failure occurs.
IoT data enhances asset visibility, reduces risk, and optimizes asset operations.
2. Big Data Analytics
The large quantities of data produced by IoT sensors undergo big data analytics. An analysis of the data is conducted to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies, thereby revealing the performance and health of the asset.
For example, if the pump regularly exhibits a pressure drop, the analytics will indicate to the engineers that they should analyze the pump before it fails.
Big data analytics converts raw information into actionable insight, so decision-makers can maximize performance and minimize waste.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are the factors behind IAPM. They analyze data to predict failures, provide maintenance advice, and even automatically recommend the optimal performance for the asset.
Machine learning models become increasingly intelligent over time as they train on historical data. They can identify risks that may not be apparent and forecast when an asset is likely to require maintenance.
Gartner predicts that predictive maintenance analytics capabilities using AI could lead to reduced maintenance costs by up to 20% and reduce unplanned downtime by 50% — a significant impact in any industrial operation.
4. Cloud Computing
All the data gathered from different assets is stored and processed using cloud platforms. Cloud computing offers the potential for scalability and allows organizations to access their asset data from virtually anywhere.
Not only does cloud computing facilitate data security, but it also promotes communications and collaboration across teams in different locations. Cloud-based asset management can also eliminate IT costs associated with high-end on-premises servers.
5. Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual representation or model of a tangible real-world asset. Digital twins simulate the behavior of the real-world asset and help operators visualize how the asset may behave under diverse conditions.
For instance, engineers could test how changing temperatures or pressures would affect the equipment’s operation, without needing to touch the actual machine.
Digital twins can also enhance the prediction accuracy of predictive maintenance and provide new operational information to companies, enabling them to incorporate it into decision-making.
Benefits of Intelligent Asset Performance Management
IAPM provides various advantages that affect cost, efficiency, and productivity. The key benefits are:
1. Enhanced Reliability of Assets
With IAPM, assets are monitored, allowing team members to be alerted to potential problems. By viewing an asset in real-time, reliability is improved, and you can avoid service interruptions or unwelcome breakdowns, leading to a smoother production flow.
2. Diminished Maintenance Costs
Routine maintenance is often scheduled based on time or usage rather than the actual condition of the asset. Therefore, some level of maintenance performed at regular intervals may not be necessary. IAPM’s predictive maintenance approach only performs an evaluation when needed, saving time, labor, and spare parts from unnecessary resource consumption.
3. Improved Operational Efficiency
The better an asset performs, the better the operations team performs. Having both real-time insight into the performance of assets allows a manager to make quick adjustments, improve performance and efficiency, and reduce energy consumption.
4. Extend Equipment Life Span
With proper maintenance and by limiting wear and tear on a machine or machine tool, the life of the asset can be extended beyond its original factory life. Timely maintenance and proper use of the machine or tool will reduce the cost per operating hour, thereby increasing the return on investment for an expensive asset.
5. Data-Driven Decision-Making
IAPM enables organizations to make informed/educated decisions based on data. For example, analytic data may show which machine is a below-average performer. If the machine that identified as below average, the operations manager can plan and replace or upgrade it using data rather than speculation.
6. Improved Safety and Compliance
Monitoring performance and catching problems early with IAPM reduces accidents. Additionally, IAPM gives assurance that safety standards and maintenance protocols are being adhered to.
Statistics That Prove IAPM Works
- The IoT in Manufacturing Market is projected to reach $3.3 trillion by 2030 (Statista).
- Predictive maintenance can decrease maintenance costs by 20% (Gartner). Firms utilizing a predictive, AI-based system have reported a 25% reduction in inspection costs (McKinsey & Co.).
These numbers suggest how Intelligent Asset Performance Management leads to both cost savings and efficiency improvements.
How IAPM Works in Real Life
Let’s talk about an automotive manufacturing facility. Each line features equipment equipped with IoT sensors that measure temperature, vibration, and speed. If a piece of equipment starts to get too hot, the system will analyze the data using AI while comparing it against historical data trends. It can predict that a failure is imminent within the next few days and will send an alert to the maintenance team.
By the time the maintenance team responds, the predicted failure has already been addressed, preventing any impact on production and thereby preserving valuable time, money, and production capacity.
That is IAPM in practice: smart, proactive, and efficient asset maintenance.
Future Trends in Intelligent Asset Performance Management

The pace of technological change is rapid, and IAPM will adapt to it. Below are some trends tracked for transformation:
- Blockchain Integration: Blockchain will help provide clarity and faith in asset data by offering permanent records of performance and maintenance.
- Edge Computing: Processing data at the edge, or source, helps minimize lag time and maximize the speed of decisions, which is particularly important for time-sensitive industries.
- Sustainability and Green Operations: IAPM will assist companies in optimizing energy usage and reducing waste, helping them meet sustainability goals and build eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
- Integration with Smart Factories: In Industry 4.0, IAPM will interface with automation systems, robotics, and digital twins to build brilliant factories.
- Advanced Predictive Analytics: Future IAPM systems will leverage deeper AI models to detect even the most subtle performance deviations — while simultaneously providing more accurate and rapid predictions.
Comparison: Traditional vs Intelligent Asset Management
| Feature | Traditional | Intelligent |
| Approach | Reactive | Predictive |
| Tech | Manual | IoT, ML, Cloud |
| Data | Delayed | Real-time |
| Maintenance | Fixed schedule | Condition-based |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Decisions | Experience-based | Data-driven |
How to Build an Effective APM Program
Establishing an effective Asset Performance Management (APM) initiative will help organizations enhance reliability, minimize downtime, and maximize the benefits of maintenance. Here are the steps to developing a successful APM program:
1. Identify Your Most Important Assets
Figure out which assets make the most significant impact on production, safety, or revenue. Focus on costly, heavily utilized, or critical assets to the operation. This will ensure that, as your APM program matures, you will get the best value and efficiency.
2. Implement APM Software with Condition Monitoring Capabilities
Select an APM software platform that incorporates condition monitoring and analysis capabilities into its core structure. Condition monitoring reduces the demand for labor hours, ensures asset performance is recorded, grasps abnormal events, and provides advanced notifications of alerts to minimize the chance of failure occurring. Additionally, IoT sensors installed on the asset can monitor temperature, vibrations, and pressures in real-time, providing alerts that can be accessed from anywhere in the world through a cloud-sharing dashboard.
3. Utilize Preventive and Predictive Maintenance Strategies
Utilize preventive maintenance, which can involve either servicing or inspection, as well as predictive maintenance driven by Artificial Intelligence and analytics. While preventive maintenance minimizes the incidence of common breakdowns, predictive maintenance can help an organization predict asset repair behavior by analyzing data. After all, minimizing unplanned breakdowns and maintenance costs is the goal.
4. Train Teams and Encourage Collaboration
A successful Asset Performance Management (APM) program relies on high-quality teams. Train technicians, engineers, and operators in the APM software, enabling them to understand the meaning of insights gleaned from the software and take action on actionable insights within the appropriate timeframe. Promote teamwork among teams performing maintenance and those performing operations, so they work together to produce actionable insights distributed across an organization that includes the shared use of performance by both maintenance and operations.
5. Monitor and Continuously Improve
Monitor and improve your APM program using key performance indicators (KPIs) directly related to your types of operations, such as metrics like equipment uptime, reduction in maintenance costs, and failure rates. You can use the KPIs to develop insights for adjusting processes or KPI adjustments to scale the APM system across an increasing number of assets when you have more time.
Conclusion
Intelligent Asset Performance Management is transforming the way industries operate by reconfiguring existing asset maintenance into a prospective, insight-based activity. It enables organizations to continuously monitor the health of its assets, anticipate potential failure events, and make informed decisions that reduce expenditure and enhance reliability. By using the availability of systems and applications integrated with IoT data, AI, and analytics, IAPM enables organizations to operate at greater efficiency and prolong the life of their assets.
It also lowers risk by increasing safety and sustainability, and promotes operational transparency. The future of work in a digital world is here, and adopting IAPM is no longer an option; it is essential for remaining competitive and adaptable.
FAQS
What do you mean by asset performance management?
This method utilizes data and provides analytics, which can help monitor, preserve, and improve the reliability of assets and minimize costs and downtime
What is the difference between SAP IAM and APM?
SAP IAM (Intelligent Asset Management) is the SAP package of digital tools that help collaborate to manage assets using AI and IOT, whereas APM is the larger concept of analyzing and improving the performance of an asset across any potential system or platform.
What is Performance Asset Management
Performance asset management is focused on making assets perform better by utilizing analytics, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance to maximize efficiency, safety, and return on investment.
What are the four pillars of PMS?
The four pillars of Performance Management Systems (PMS) are planning, monitoring, developing, and rating in order to effectively track and improve the performance of assets and employees.
What are the five stages of asset management?
The five stages of Asset Management are development, acquisition, operation, maintenance, and disposal to guarantee the asset realizes the greatest value throughout its lifecycle.

