Artificial intelligence has moved beyond the realm of fiction and is now a reality that people experience in their daily lives. Thus, AI is already present in almost every aspect of human activities. A smartphone user, a viewer of suggested videos, and a reader of AI-generated content are all in contact with modern technology. Generative AI, among all the innovations, has reached the peak of AI technology. It can generate new text, pictures, music, videos, and even computer code through simple data learning.
This publication clarifies the concept of generative AI by analyzing its workings, applications, advantages, and drawbacks. The main aim is to give readers a clear understanding of the technology and provide them with the tools to harness its benefits.
What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to systems that can produce new content based on patterns learned from existing data. Unlike traditional AI, which typically analyzes and predicts outcomes from data, generative AI generates entirely new outputs that did not exist before.
These systems rely on machine learning models—computer programs designed to recognize patterns and replicate certain aspects of human intelligence. Generative AI models can create:
- Text (like articles, stories, or emails)
- Images (digital art, designs, or photorealistic visuals)
- Audio (music, speech, or sound effects)
- Code (software scripts or programming solutions)
- Videos and animations
The AI generative models people talk about most are ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Midjourney, all from OpenAI. To put it differently, each tool proves an ability to generate content almost indistinguishable from that of a human being in its area of competence.
How Generative AI Works
Generative AI follows a multi-step process: data processing, user input, and content generation. The following is the sequential explanation of it:
Step 1: Training the Model
Generative AI models learn from enormous datasets. Those datasets may contain text, images, audio, or even code. The model learns.
- patterns
- structures
- relationships
- styles
- rules
- context
For example:
- An image model, on the other hand, learns to identify shapes, colours, textures, and design patterns by being exposed to millions of images.
- An image model learns to recognise shapes, colours, textures, and design patterns from millions of images.
The more data the model learns from, the better it becomes at generating realistic output.
Step 2: Processing User Prompts
After completing its training, the AI is ready to generate new content in response to user prompts. A prompt is basically a set of guidelines or questions that control the AI’s output. For example:
- Text prompt: “Write a 150-word description of a futuristic electric car.”
- Image prompt: “Create a digital painting of a serene mountain landscape at sunset.”
The AI uses its training knowledge to generate content that aligns with the prompt.
Step 3: Generating Content
Once the prompt has been analysed, the AI uses various techniques to generate new content. The three most frequently employed generative approaches are as follows:
1. Large Language Models (LLMs)
The models anticipate the subsequent word in a statement. Their continuous operation can result in the production of lengthy, coherent text akin to that of a human. ChatGPT and GPT-based models utilize this technique.
2. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs use two neural networks:
- Generator: Creates new images
- Discriminator: Judges whether the images look real
Competing networks keep doing that until, after a while, the outcome is simply unbelievably real. GANs have been employed in the domains of generating artificial photos and deepfakes.
3. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
VAEs manage the tasks of compressing and reconstructing data. Consequently, they can produce new images and designs. They serve purposes in areas such as graphics, coding, and design optimisation.
Applications of Generative AI

Generative AI is not merely a technological wonder—it brings forth a variety of applications in many industries worldwide:
Content Creation
Companies and artists use generative AI to write articles, prepare marketing materials, and compose social media posts. AI tools can significantly speed up the content creation process by providing a consistent tone and style.
Marketing and Advertising
AI-assisted tools not only produce ad copy, but also headlines, product descriptions, and sometimes even campaign visuals. They enable marketers to experiment with variations and promptly promote the content most likely to drive the highest engagement.
Healthcare
Generative AI is a valuable tool in medical research, encompassing drug discovery, genome sequencing, and medical imaging analysis. It can provide synthetic data for training, thereby enhancing precision and reducing costs.
Automotive and Engineering
Generative AI has become a major player in the design optimisation game, enabling manufacturers to develop parts and systems with greater efficiency and performance.
Entertainment and Media
In the gaming, film, and virtual reality sectors, AI-generated visuals, music, and animations are increasingly replacing human artists, speeding up production without sacrificing quality.
Benefits of Generative AI
Generative AI gives a lot of benefits to both people and companies:
1. Saves Time and Money
Businesses can create content, designs, and solutions in minutes rather than hours or days.
2. Boosts Creativity
AI gives new ideas, styles, and innovations, helping humans think beyond traditional limits.
3. Maintains Consistency
AI can produce content with the same tone, style, and structure across many platforms.
4. Helps Small Businesses Compete
Small teams can still produce high-quality designs, ads, and content like a big creative department without hiring a single person.
5. Makes Complex Tasks Simple
It can capture the essence of long documents, expound on complex topics, and even make comprehensive plans.
Limitations and Challenges of Generative AI
Despite its benefits, generative AI has limitations:
- Accuracy Issues: AI may produce content that contains errors or misleading information.
- Bias and Ethics: Models may reflect biases present in training data.
- Lack of Original Thought: AI does not create truly independent ideas; it relies on patterns learned from existing data.
- Resource Intensive: Training and running AI models require substantial computing power.
Moreover, users still have to double-check the outputs to ensure accuracy and trustworthiness. Ethical issues, such as deepfakes and falsehoods, will remain significant hurdles.
What is the difference between OpenAI and generative AI?
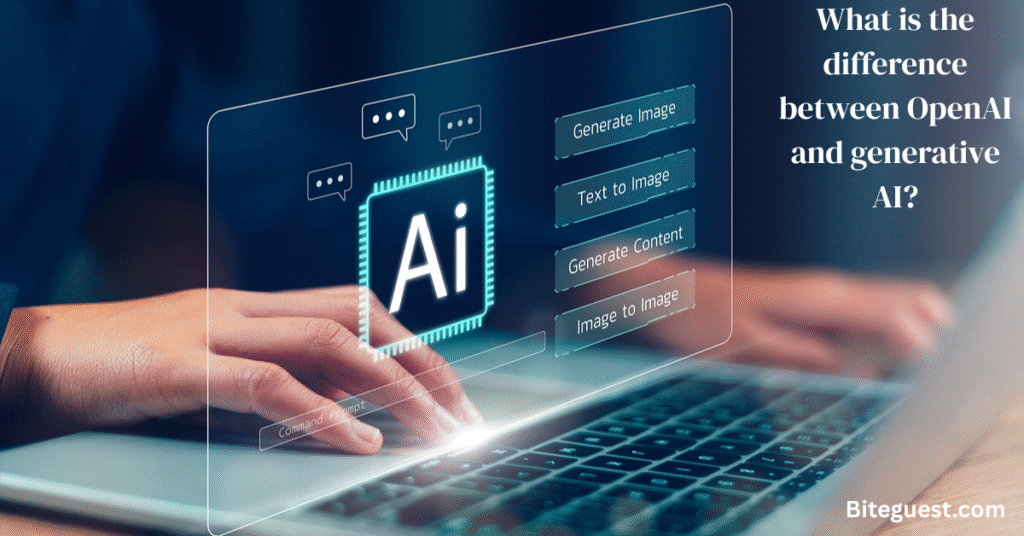

| Feature | OpenAI | Generative AI |
| Type | Company | Technology / AI type |
| Purpose | Develops AI tools and models | Creates new content (text, images, audio, video) |
| Examples | ChatGPT, DALL-E | GPT, GANs, VAEs |
| Function | Builds and deploys AI applications | Generates content using machine learning models |
| Scope | Specific organization | A broad category of AI technologies |
| Focus | AI research, safety, and applications | Content generation and creativity |
“Generative AI vs. Traditional AI: Key Differences Explained”
Generative AI
- Creates new content
- Learns from large datasets
- Examples: GPT, DALL-E, Midjourney
- Creative and flexible
Specific AI (Narrow AI)
- Designed for a particular task
- Rule-based and precise
- Examples: spam filters, recommendation engines
- Cannot create new content
Specific AI is useful for focused tasks, while generative AI is useful for creativity and content generation.
Future of Generative AI
The generative AI has a bright future ahead. Experts foresee significant developments in various fields:
1. Wider Adoption
Generative AI will become more prevalent across all businesses as more industries embrace it for content creation, design, automation, and customer service.
2. Better Prompting Techniques
Users will learn how to write more advanced prompts to get high-quality results.
3. Cross-Modal AI
Multiple types of AI content will be managed together, for example, transforming text into video and audio into images.
4. Stronger AI Detection Tools
Tools will improve to detect AI-generated content and reduce the risk of deepfakes.
Conclusion:
The technology is already one of the great tools of the 21st century. It is an exceptional creator, problem-solver, and a great supporter of learning. Knowing the technology and how it operates gives one the power to use it effectively. The more you learn about it, the clearer its strengths and weaknesses become; this, in turn, helps you choose the right technology and get maximum results. If you want to be at the top of the modern world, learning technology is key to getting ahead. It will be an ongoing process, and those knowledgeable about it will definitely hold the upper hand.
FAQS
Can generative AI fully replace human creativity?
No. AI assists creativity, but human input is essential for originality and critical thinking.
What types of content can generative AI produce?
It can generate text, images, audio, videos, code, animations, and simulations.
Are there risks associated with generative AI?
Yes. Risks include bias, misinformation, ethical concerns, and over-reliance on AI outputs.
How can businesses benefit from generative AI?
Generative AI increases productivity, boosts human creativity, and enables the creation of large amounts of high-quality content.

